When I think about LEGO, I think about brightly colored bricks and detailed minifigures decorated with vivid patterns. These patterns are not simple stickers; they are actual prints on the plastic. Over time, many have wondered: does LEGO rely on traditional pad printing techniques or has it adopted UV printing methods? This question touches upon how LEGO manages to maintain consistent quality, durability, and intricate details in their products.
[Table of Contents]
- 1. LEGO’s Printed Patterns: A Brief History
- 2. What is Pad Printing?
- 3. What is UV Printing?
- 4. Why Does LEGO Prefer Pad Printing?
- 5. Comparing Pad Printing and UV Printing
- 6. Scaling Up: Mass Production and Efficiency
- 7. Quality Control and Standards
- 8. Customization and Special Editions
- 9. Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
- 10. Future Outlook
- 11. Conclusion
1. LEGO’s Printed Patterns: A Brief History
LEGO printing has evolved dramatically since its early days. In the beginning, LEGO bricks featured basic logos or simple markings. Gradually, as the brand expanded its universe of sets, minifigures, and stories, the need for more detailed printing methods grew. Initially, these prints were rudimentary, often single-color applications. However, as fans demanded more realistic characters, intricate torso designs, and unique elements to tell richer stories, LEGO continuously refined its printing methods.
By the time minifigures rose to popularity in the late 1970s and early 1980s, LEGO had developed consistent, high-quality printing solutions capable of producing detailed patterns. Over subsequent decades, as themes like Star Wars, Harry Potter, and Marvel joined the LEGO family, the complexity and quality of prints skyrocketed. This journey reflects how LEGO adopted and improved upon various printing techniques, eventually arriving at a reliable and reproducible method that meets strict quality standards.

The central debate that often arises among collectors and curious enthusiasts is whether LEGO currently uses pad printing or UV printing for their bricks and minifigures. The short answer: LEGO predominantly uses pad printing for its official products. Yet, to understand why this is the case, it’s essential to dive into the details of what pad printing is, how it compares to UV printing, and what each method entails in terms of quality, cost, and feasibility.
2. What is Pad Printing?
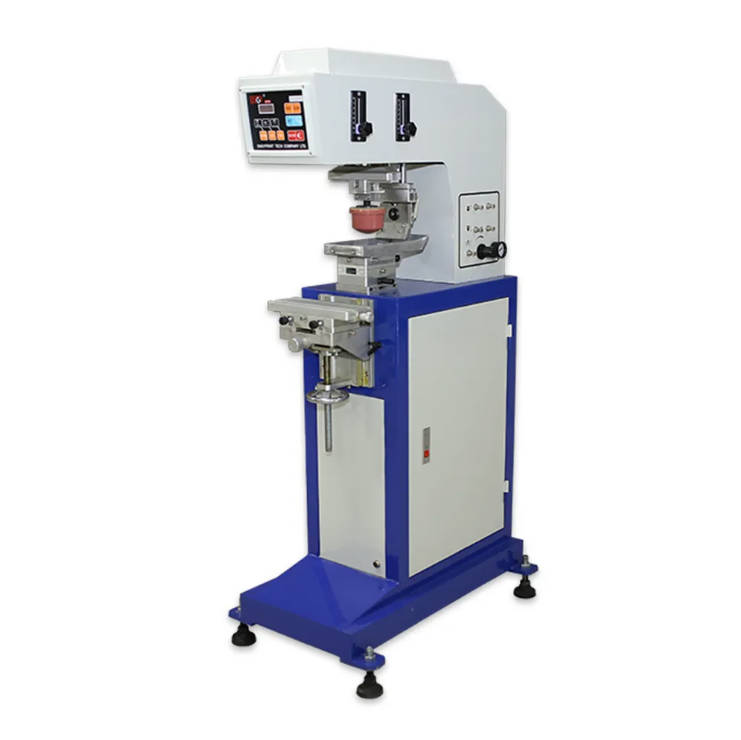
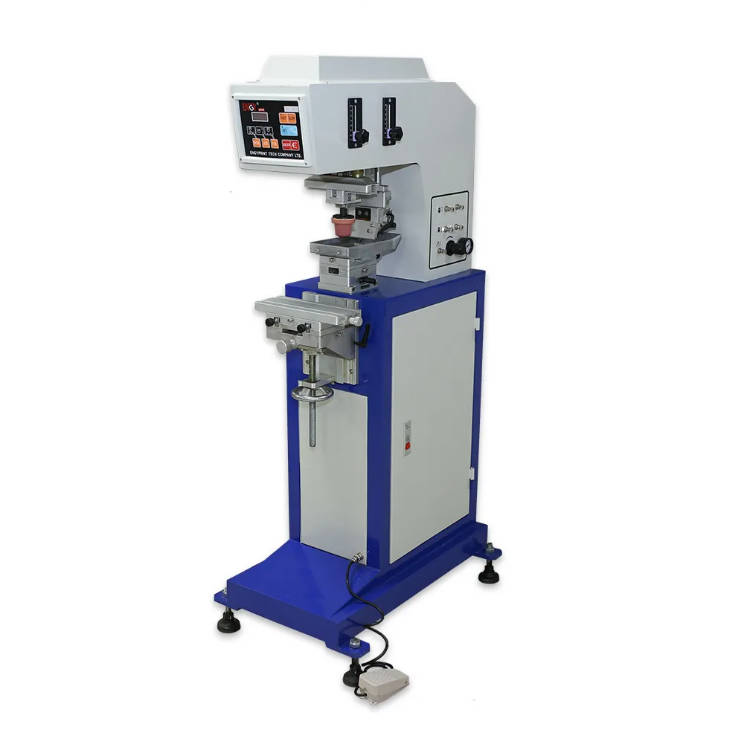
Pad printing, also known as tampography, is a widely used technique to transfer inked images from a silicone pad onto an object. It is particularly effective for printing on irregularly shaped surfaces—like the curved torso of a LEGO minifigure or the sloped shape of a brick. The process involves etching a design into a plate, filling it with ink, and then using a soft silicone pad to pick up the ink and transfer it onto the target surface.
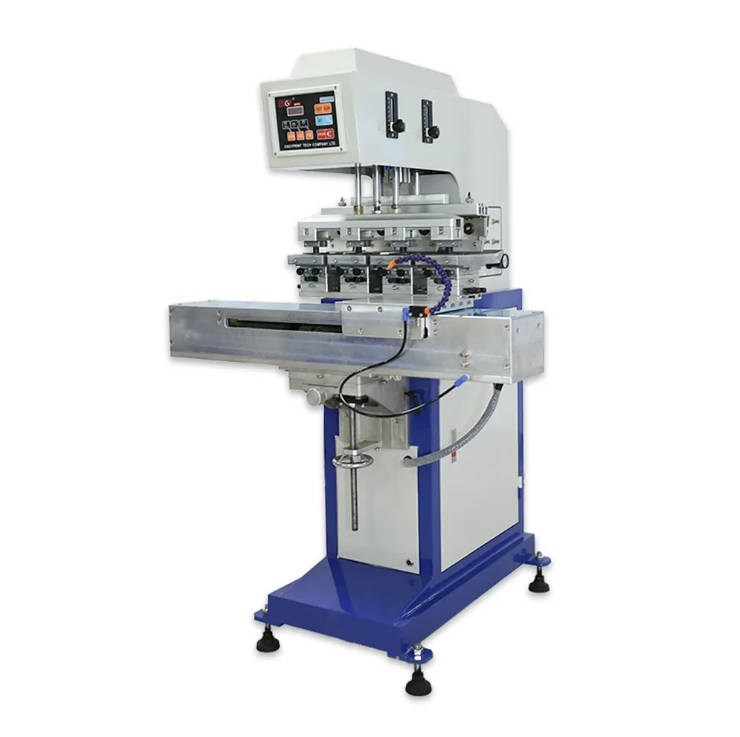
A key strength of pad printing lies in its precision and repeatability. Using a dedicated pad printing machine, manufacturers can apply multiple colors sequentially, ensuring alignment and consistency. This technique is relatively fast and reliable, making it ideal for large-scale production. In the world of LEGO, the use of a specialized pad printer, along with proper pad printing supplies and pad printing equipment, ensures that each minifigure’s torso or each decorative brick turns out with consistent quality.
Pad printing also supports a wide range of inks, including those formulated for robust adhesion to ABS plastic (the primary material for LEGO bricks). By carefully selecting inks and controlling the production environment, pad printing achieves vibrant, durable prints that withstand play and wear. Given LEGO’s global reach and massive manufacturing volumes, pad printing fits well into a fully automated system. Indeed, LEGO often employs an automatic pad printing machine, integrated into its production lines, achieving both efficiency and precision.
How Pad Printing Works in Steps
1. A steel or aluminum plate is engraved with the desired pattern.
2. Ink fills the etched pattern.
3. A silicone pad presses onto the ink-filled plate, picking up the ink.
4. The pad then transfers the ink onto the LEGO piece.
5. The printed piece undergoes drying and quality checks.
| Component | Function | Notes |
| Pad Printing PLC or PCB board | Controls the printing process | Ensures precise, consistent transfers |
| Pad Printer pad fixture | Holds the silicone pad | Moves between ink plate and LEGO piece |
| Pad Printing Supplies | Inks, plates, pads | Selected for compatibility and longevity |
| Pad Printing Equipment | All supportive tools | Fixtures, cleaning tools, alignment systems |
| Automatic Pad Printing Machine | Fully automated line | High throughput for mass production |
This well-established process has proven itself in numerous industries, from promotional products to medical devices. For LEGO, pad printing represents a tried-and-true method that aligns perfectly with the brand’s emphasis on precision, consistency, and durability.
3. What is UV Printing?
UV printing is a more modern digital printing method where specially formulated inks are cured (dried) almost instantly using ultraviolet light. Unlike pad printing’s mechanical process, UV printing can often apply designs in a more direct-to-substrate fashion, potentially reducing setup times and enabling faster design changes. With UV printing, a print head deposits the ink onto the surface, and a UV lamp immediately cures it, creating a durable, vibrant print.
One might think UV printing would be ideal for LEGO—after all, it’s flexible and can produce detailed images. Yet, UV printing has its own limitations. While it can achieve remarkable detail, UV printing often struggles to match the consistency and tight tolerances required for LEGO parts. The shape and texture of LEGO elements, as well as the complexity of applying precise alignment across millions of pieces, mean that UV printing may not integrate as seamlessly into LEGO’s highly automated and quality-focused production lines.
UV printing may also present challenges in ink adhesion and color matching over time. Although UV inks are durable, the mechanical handling of LEGO bricks and the rigorous play they endure mean any deviation in adhesion or ink thickness could lead to print wear or inconsistent finishes. While smaller manufacturers or custom shops sometimes use UV printing to personalize LEGO pieces, LEGO itself tends to favor pad printing for mass production.
4. Why Does LEGO Prefer Pad Printing?
LEGO’s choice to rely on pad printing can be understood by examining several key factors. First, pad printing excels at producing uniform, long-lasting results at enormous scales. LEGO runs multiple production lines, each churning out millions of identical components. Pad printing integrates neatly into this environment, ensuring that every piece—whether it’s a standard brick, a minifigure torso, or a rare decorative element—meets strict quality standards.
Second, pad printing’s ability to handle curved and uneven surfaces is essential. LEGO minifigures, for example, have torsos, heads, and legs with subtle shapes that might pose a challenge to flat-bed printing methods like UV printing. Pad printing’s flexible silicone pad can conform to these shapes, transferring ink accurately and consistently.
Moreover, pad printing machines and automatic pad printing machines can be finely tuned. This ensures the ink’s thickness, color saturation, and alignment remain stable. LEGO’s brand reputation hinges on offering products that look the same, set after set. Any slight variation could disappoint discerning fans. The proven track record of pad printing assures LEGO that each product meets their consumers’ high expectations.
Critical Points that Drive LEGO’s Decision
- Consistency across millions of parts
- Adaptability to curved, irregular surfaces
- Long-term reliability and durability
- Integration with automated production systems
Deeper Insight: Beyond Just a Printing Method
LEGO’s preference is not only technical but also strategic. They’ve built a complex supply chain with pad printing at its core. Switching to UV printing would require substantial changes, from ink formulations to machine setups. While LEGO constantly innovates, they also value stable, proven methods to guarantee product integrity. Thus, pad printing remains their go-to solution.

5. Comparing Pad Printing and UV Printing
To understand LEGO’s choice fully, let’s compare key attributes of pad printing and UV printing. Both methods have their strengths, but when it comes to producing millions of perfectly identical bricks and minifigures, one method may outshine the other.
Precision and Detail
Pad printing has developed over decades, achieving fine detail and crisp lines. UV printing can also produce detailed images; however, ensuring perfect alignment on 3D surfaces might not be as straightforward. LEGO sets often have tiny facial features or intricate patterns. Pad printing’s controlled mechanical transfer ensures these features remain sharp and consistent.
Durability and Resistance
LEGO pieces face rough treatment—children build, rebuild, and mix sets frequently. Prints must withstand friction, handling, and even exposure to elements. Pad printing inks and curing methods have been optimized for this. UV inks are tough, but differences in thickness or adhesion could appear under high-volume runs. Over time, pad printing’s reliability in delivering uniform thickness and adhesion often wins out.
Production Speed and Scale
At LEGO’s scale—producing billions of elements annually—efficiency is crucial. Pad printing lines are well-oiled machines with predictable outputs. Introducing UV printing might slow production or complicate workflow. Pad printing equipment is specifically tailored to handle huge volumes without compromising quality.
Cost and Complexity
UV printing equipment might seem modern and versatile, but adopting it for millions of identical pieces may involve complex calibrations and higher operational costs. Pad printing is a known quantity, minimizing unexpected expenses and downtime. With an automatic pad printing machine in place, LEGO can maintain efficiency and manage costs effectively.
| Factor | Pad Printing | UV Printing |
| Alignment on 3D surfaces | Excellent, pad adapts to shape | More challenging, flat-based |
| Durability | Highly durable inks | Durable but dependent on perfect adhesion |
| Volume Integration | Proven large-scale efficiency | Less established for mass volume |
| Cost | Predictable, lower long-term cost | Potentially higher setup and calibration costs |
| Adaptability | Mature process, well-known | Flexible digitally, but less proven for LEGO scale |
Overall, while UV printing is excellent for certain niche applications or rapid prototyping, pad printing hits the sweet spot for LEGO’s massive scale and exacting standards.
6. Scaling Up: Mass Production and Efficiency
LEGO’s production lines are marvels of efficiency. They run around the clock to ensure that every set released worldwide meets demand. At such scale, consistency is king. Pad printing fits perfectly here, offering a stable, reproducible method that can easily be integrated into automated workflows.
The role of an automatic pad printing machine is crucial. Automated systems reduce human error, maintain steady production rates, and ensure that every brick is printed identically. This level of control means that from the first brick to the millionth, quality does not waver. Although UV printing might seem appealing for customization or short runs, it’s not yet proven at the scale LEGO commands.
Automated Systems in Action
In a typical production run, robots feed bricks into the printing station. The automatic pad printing machine applies the ink in multiple steps if needed—one color at a time. Sensors check alignment, and if a part is off, the machine can reject it. The output is a continuous stream of perfectly printed parts, ready to be packed and shipped. Any disruption in this process could cost time and money, so LEGO invests in maintaining a stable and tested technology.
Supply Chain Considerations
LEGO’s factories are located worldwide, from Denmark to the Czech Republic, Hungary, Mexico, and China. Each facility coordinates to produce parts that come together in sets. Pad printing’s well-understood requirements help ensure consistency across these facilities. Shared knowledge, standardized ink formulations, and uniform pad printing supplies streamline operations. Introducing UV printing would require re-engineering processes, training staff, and testing new materials, potentially disrupting the established equilibrium.
In short, for mass production, pad printing is not just a printing technique; it’s a pillar supporting LEGO’s global manufacturing strategy.
7. Quality Control and Standards
LEGO takes quality seriously. They know that their customers expect perfect prints every time—no smudges, no misalignment, no fading. Achieving this standard demands rigorous quality control measures. Pad printing processes are thoroughly tested, from ink chemistry to curing times, to ensure the final print is flawless.
In a pad printing workflow, each step can be monitored. The plate’s etching depth, the ink’s viscosity, the pad’s firmness, and the machine’s speed all contribute to final results. By refining and standardizing these parameters, LEGO ensures that whether a piece is produced in Europe or Asia, it adheres to the same exacting quality benchmarks.
Color Consistency
One hallmark of LEGO’s commitment to quality is consistent color. The red on a LEGO firefighter’s torso should match the red on a LEGO brick produced years apart. With pad printing, color formulation is stable, and inks are meticulously blended. UV printing might face variability due to different ink sets, curing intensities, or substrate conditions.
Long-Term Reliability
LEGO sets are often passed down generations. Pad printing ensures that graphics remain intact for decades if stored and handled reasonably. UV printing, while durable, hasn’t been tested by LEGO at the same scale and time frames. Maintaining brand reputation requires a proven process that’s delivered consistent quality over many years.
Quality control ensures not just a single print run, but the entire product line meets LEGO’s unparalleled standards. Pad printing provides a stable foundation for these stringent controls.
8. Customization and Special Editions
While LEGO primarily focuses on mass production, there is a growing community of fans who customize bricks. These fans often turn to UV printing for short-run custom designs or special patterns. For instance, a fan might want a custom-printed minifigure with a unique logo or artwork. Small-scale print shops or hobbyists can adopt UV printing for these bespoke projects, thanks to its flexibility and lower initial setup.
However, when LEGO itself produces limited-edition sets—like a promotional figure at a fan event or a collector’s edition minifigure—they still rely on pad printing. This ensures that even these rare items maintain the same quality and durability as standard sets. Special editions might have more complex multi-color prints, and pad printing accommodates this by applying each color layer with perfect registration.
Dive Deeper: Hobbyists and Third Parties
Many hobbyists who create custom LEGO elements embrace UV printing because it allows them to produce small batches without the complexity of engraving plates or managing inks as in pad printing. For them, UV printing offers speed and adaptability. Yet, these small operations don’t face LEGO’s massive scale or stringent uniformity requirements.
Customization Table
| Factor | Hobbyist UV Printing | LEGO Pad Printing |
| Scale | Small runs | Massive production |
| Setup Cost | Lower for small projects | Higher initial but efficient at scale |
| Consistency | Varies with operator skill | Uniform and standardized |
| Durability | Good but less tested | Proven longevity |
Ultimately, UV printing thrives in the niche of customization, while pad printing dominates standardized, large-scale production.
9. Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
As companies focus more on sustainability, printing methods also come under scrutiny. LEGO has pledged to reduce environmental impact, from using bio-based plastics to improving packaging. While printing might seem a minor aspect, it still requires ink, energy, and equipment maintenance.
Pad printing has been refined over decades to minimize waste. Inks are precisely measured, and automated systems reduce errors, thus limiting rejects. UV printing, by contrast, introduces a different set of environmental considerations. UV inks can be more difficult to dispose of responsibly, and the curing process involves UV lamps that consume energy.

While the environmental difference might not be vast, any change in printing technology would require LEGO to reassess its entire supply chain and manufacturing processes. Sticking with pad printing means working with known parameters and continuously optimizing them. If UV printing someday offers a clearer environmental advantage while meeting quality standards, LEGO might consider it. But currently, pad printing aligns well with LEGO’s established sustainability initiatives.
Critically Assessing Environmental Factors
In the broader picture, the main environmental impact of LEGO’s business comes from raw materials and shipping rather than printing. Still, every improvement counts. Pad printing’s long history provides a platform for incremental environmental improvements. UV printing, as a newer method, might need more research to ensure it fits into a long-term sustainability strategy.
10. Future Outlook
Will LEGO ever switch to UV printing or another emerging technology? While it’s hard to predict the future, LEGO continuously experiments. They might test UV printing on specific products or implement hybrid approaches. As digital printing technologies evolve, some of the drawbacks currently preventing widespread UV adoption might diminish.
However, any shift must maintain or improve the hallmark quality, consistency, and durability that LEGO fans expect. New inks must adhere as well as current ones; production lines must run smoothly without increasing costs or downtime; and color fidelity must remain impeccable. If a future technology can deliver on these promises while offering even greater efficiency or environmental benefits, LEGO could consider integrating it.
Emerging Technologies
- Digital inkjet methods adapted to 3D surfaces
- Advanced UV-curable inks optimized for ABS plastic
- Robotic systems with vision-based alignment
- Eco-friendly inks derived from renewable sources
For now, pad printing reigns supreme. But LEGO’s history shows it’s not afraid to innovate. As fans demand even more detailed prints, new materials appear, and automation tools improve, LEGO might explore more sophisticated print technologies. The question is not just about UV printing; it’s about what the future of manufacturing holds.
11. Conclusion
At present, LEGO relies primarily on pad printing to achieve its iconic, high-quality patterns on bricks and minifigures. While UV printing and other methods exist, the consistency, durability, and scalability of pad printing remain unmatched. Supported by a suite of pad printing equipment, pad printing supplies, and even the use of an automatic pad printing machine, this method ensures every LEGO piece meets the brand’s timeless standards.
In other words, if you’re holding a freshly opened LEGO minifigure with a crisp, vibrant design, chances are that print was applied using pad printing technology—reinforcing LEGO’s longstanding commitment to quality and excellence.





